Backup and Restore
Reference
- https://milvus.io/blog/how-to-use-milvus-backup-tool-step-by-step-guide.md#Preparation
- https://milvus.io/docs/milvus_backup_overview.md
- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zilliztech/milvus-backup/master/configs/backup.yaml
- https://milvus.io/docs/milvus-cdc-overview.md
Milvus-backup Tool
Milvus-backup is a data backup and recovery tool specifically developed by Zilliz for Milvus.
Milvus-backup supports the following capabilities:
- Supports multiple interaction methods including command line and Restful API;
- Supports hot backup with minimal impact on Milvus cluster operations;
- Supports full cluster backup or specified collection backup;
- Achieve backup and recovery through bulkinsert, with the option to rename collections during recovery;
- Supports S3, cross-bucket backup, enabling migration between clusters;
- Compatible with Milvus versions 2.2.0 and above;
- Currently only supports backing up metadata, not index data.
Command Overview
- General Help: Type
milvus-backup helpto view the available commands and flags.milvus-backup is a backup&restore tool for milvus.
Usage:
milvus-backup [flags]
milvus-backup [command]
Available Commands:
check check if the connects is right.
create create subcommand create a backup.
delete delete subcommand delete backup by name.
get get subcommand get backup by name.
help Help about any command
list list subcommand shows all backup in the cluster.
restore restore subcommand restore a backup.
server server subcommand start milvus-backup RESTAPI server.
Flags:
--config string config YAML file of milvus (default "backup.yaml")
-h, --help help for milvus-backup
Use "milvus-backup [command] --help" for more information about a command. - Creating a Backup: Get specific help for creating a backup by typing
milvus-backup create --help.Usage:
milvus-backup create [flags]
Flags:
-n, --name string backup name, if unset will generate a name automatically
-c, --colls string collectionNames to backup, use ',' to connect multiple collections
-d, --databases string databases to backup
-a, --database_collections string databases and collections to backup, json format: {"db1":["c1", "c2"],"db2":[]}
-f, --force force backup, will skip flush, should make sure data has been stored into disk when using it
--meta_only only backup collection meta instead of data
-h, --help help for create - Restoring a Backup: To understand how to restore a backup, use
milvus-backup restore --help.Usage:
milvus-backup restore [flags]
Flags:
-n, --name string backup name to restore
-c, --collections string collectionNames to restore
-s, --suffix string add a suffix to collection name to restore
-r, --rename string rename collections to new names, format: db1.collection1:db2.collection1_new,db1.collection2:db2.collection2_new
-d, --databases string databases to restore, if not set, restore all databases
-a, --database_collections string databases and collections to restore, json format: {"db1":["c1", "c2"],"db2":[]}
--meta_only if true, restore meta only
--restore_index if true, restore index
--use_auto_index if true, replace vector index with autoindex
--drop_exist_collection if true, drop existing target collection before create
--drop_exist_index if true, drop existing index of target collection before create
--skip_create_collection if true, will skip collection, use when collection exist, restore index or data
-h, --help help for restore
Backup/Restore Use Cases
There are several use cases in which the milvus-backup tool can be applied effectively, depending on your specific needs and configurations:
-
Within a Single Milvus Instance: Copy a collection to a new one within the same Milvus service.
-
Between Milvus Instances in a Single S3 with One Bucket: Transfer a collection between Milvus instances with different root paths but using the same S3 bucket.
-
Between Milvus Instances Across Different S3 Buckets: Transfer a collection between different S3 buckets within the same S3 service.
-
Across Different S3 Services: Copy a collection between Milvus instances that are using different S3 services.
Here, we only test backup and recovery within a single milvus cluster. If you need to restore from Cluster A to Cluster B, you'll need to modify the configuration file by adjusting the Milvus and MinIO connection settings. https://milvus.io/docs/milvus_backup_overview.md.
Workflow of backup and restore
Data Preparation
Collection named "quick_setup" will be created and 10 records will be inserted into it.
- Prepare
prepare-data.job.yamlapiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: milvus-prepare-job
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: pymilvus-prepare-data
image: m.lab.zverse.space/docker.io/bitnami/pymilvus:latest
command: ['python', '-c']
args:
- |
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, DataType
import os
collection_name = os.getenv("COLLECTION_NAME")
client = MilvusClient(
uri=os.getenv("MILVUS_URI"),
token=os.getenv("MILVUS_TOKEN")
)
# Create schema
schema = MilvusClient.create_schema(
auto_id=False,
enable_dynamic_field=True,
)
# Add fields to schema
schema.add_field(field_name="id", datatype=DataType.INT64, is_primary=True)
schema.add_field(field_name="vector", datatype=DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR, dim=5)
schema.add_field(field_name="color", datatype=DataType.VARCHAR, max_length=512)
# Prepare index parameters
index_params = client.prepare_index_params()
# Add indexes
index_params.add_index(
field_name="id",
index_type="AUTOINDEX"
)
index_params.add_index(
field_name="vector",
index_type="AUTOINDEX",
metric_type="COSINE"
)
# Create a collection with the index loaded simultaneously
client.create_collection(
collection_name=collection_name,
schema=schema,
index_params=index_params
)
res = client.list_collections()
print(res)
res = client.get_load_state(
collection_name=res[0]
)
print(res)
# Insert entities into collection
data=[
{"id": 0, "vector": [0.3580376395471989, -0.6023495712049978, 0.18414012509913835, -0. 26286205330961354, 0.9029438446296592], "color": "pink_8682"},
{"id": 1, "vector": [0.19886812562848388, 0.06023560599112088, 0.6976963061752597, 0. 2614474506242501, 0.838729485096104], "color": "red_7025"},
{"id": 2, "vector": [0.43742130801983836, -0.5597502546264526, 0.6457887650909682, 0. 7894058910881185, 0.20785793220625592], "color": "orange_6781"},
{"id": 3, "vector": [0.3172005263489739, 0.9719044792798428, -0.36981146090600725, -0. 4860894583077995, 0.95791889146345], "color": "pink_9298"},
{"id": 4, "vector": [0.4452349528804562, -0.8757026943054742, 0.8220779437047674, 0. 46406290649483184, 0.30337481143159106], "color": "red_4794"},
{"id": 5, "vector": [0.985825131989184, -0.8144651566660419, 0.6299267002202009, 0. 1206906911183383, -0.1446277761879955], "color": "yellow_4222"},
{"id": 6, "vector": [0.8371977790571115, -0.015764369584852833, -0.31062937026679327, -0. 562666951622192, -0.8984947637863987], "color": "red_9392"},
{"id": 7, "vector": [-0.33445148015177995, -0.2567135004164067, 0.8987539745369246, 0. 9402995886420709, 0.5378064918413052], "color": "grey_8510"},
{"id": 8, "vector": [0.39524717779832685, 0.4000257286739164, -0.5890507376891594, -0. 8650502298996872, -0.6140360785406336], "color": "white_9381"},
{"id": 9, "vector": [0.5718280481994695, 0.24070317428066512, -0.3737913482606834, -0. 06726932177492717, -0.6980531615588608], "color": "purple_4976"}
]
res = client.insert(
collection_name=collection_name,
data=data
)
print(res)
env:
- name: MILVUS_URI
value: http://milvus-577-proxy.middleware-csst.svc.cluster.local:19530
- name: MILVUS_TOKEN
value: "user:pwd"
- name: COLLECTION_NAME
value: quick_setup
restartPolicy: Never
backoffLimit: 0 - Apply
kubectl -n middleware-csst apply -f prepare-data.job.yaml
kubectl -n middleware-csst get pod
kubectl -n middleware-csst logs milvus-prepare-job-hbvkj
Backup All Collections
- Prepare
backup.job.yamlapiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: milvus-backup-config
data:
backup.yaml: |
log:
file:
rootPath: "logs/backup.log"
milvus:
address: "milvus-577-proxy.middleware-csst.svc.cluster.local"
port: 19530
user: "user"
password: "pwd"
# tls mode values [0, 1, 2]
# 0 is close, 1 is one-way authentication, 2 is mutual authentication
tlsMode: 0
# Related configuration of minio, which is responsible for data persistence for Milvus.
minio:
# Milvus storage configs, make them the same with milvus config
storageType: "minio" # support storage type: local, minio, s3, aws, gcp, ali(aliyun), azure, tc (tencent), gcpnative
address: "milvus-577-minio.middleware-csst.svc.cluster.local" # Address of MinIO/S3
port: 9000 # Port of MinIO/S3
accessKeyID: "admin" # accessKeyID of MinIO/S3
secretAccessKey: "admin" # MinIO/S3 encryption string
useSSL: false # Access to MinIO/S3 with SSL
useIAM: false
iamEndpoint: ""
bucketName: "milvus" # Milvus Bucket name in MinIO/S3, make it the same as your milvus instance
rootPath: "file" # Milvus storage root path in MinIO/S3, make it the same as your milvus instance
# Backup storage configs, the storage you want to put the backup data
backupStorageType: "minio" # support storage type: local, minio, s3, aws, gcp, ali(aliyun), azure, tc (tencent)
backupAddress: "milvus-577-minio.middleware-csst.svc.cluster.local" # Address of MinIO/S3
backupPort: 9000 # Port of MinIO/S3
backupAccessKeyID: "admin" # accessKeyID of MinIO/S3
backupSecretAccessKey: "admin" # MinIO/S3 encryption string
backupBucketName: "milvus" # Bucket name to store backup data. Backup data will store to backupBucketName/backupRootPath
backupRootPath: "backup" # Rootpath to store backup data. Backup data will store to backupBucketName/ backupRootPath
backupUseSSL: false # Access to MinIO/S3 with SSL
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: milvus-backup-job
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: milvus-backup
image: m.lab.zverse.space/docker.io/milvusdb/milvus-backup:latest
command: ['sh', '-c']
args:
- |
# All collections will be backup
./milvus-backup create -n my_backup --config /data/backup.yaml
env:
- name: MILVUS_URI
value: http://milvus-577-proxy.middleware-csst.svc.cluster.local:19530
- name: MILVUS_TOKEN
value: "user:pwd"
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /data
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: milvus-backup-config
defaultMode: 0755
restartPolicy: Never
backoffLimit: 0 - Apply
kubectl -n middleware-csst apply -f backup.job.yaml - Check
After execution, we can check the backup files via MinIO's UI. It can be seen that under the path backup (consistent with the configuration), a directory named my_backup has been created, containing two folders that store the backup metadata (meta) and the actual data (binlog) respectively.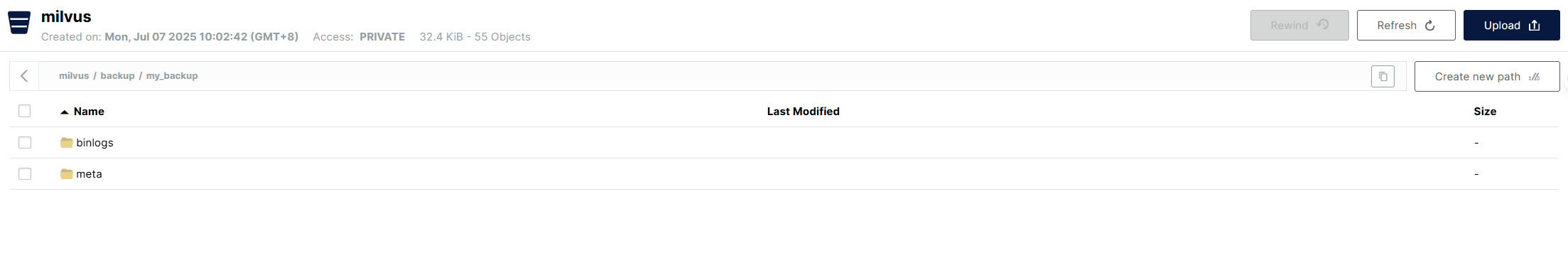 Under the meta directory are some metadata files, which record the metadata at the backup, collection, partition, and segment levels.
Under the meta directory are some metadata files, which record the metadata at the backup, collection, partition, and segment levels.
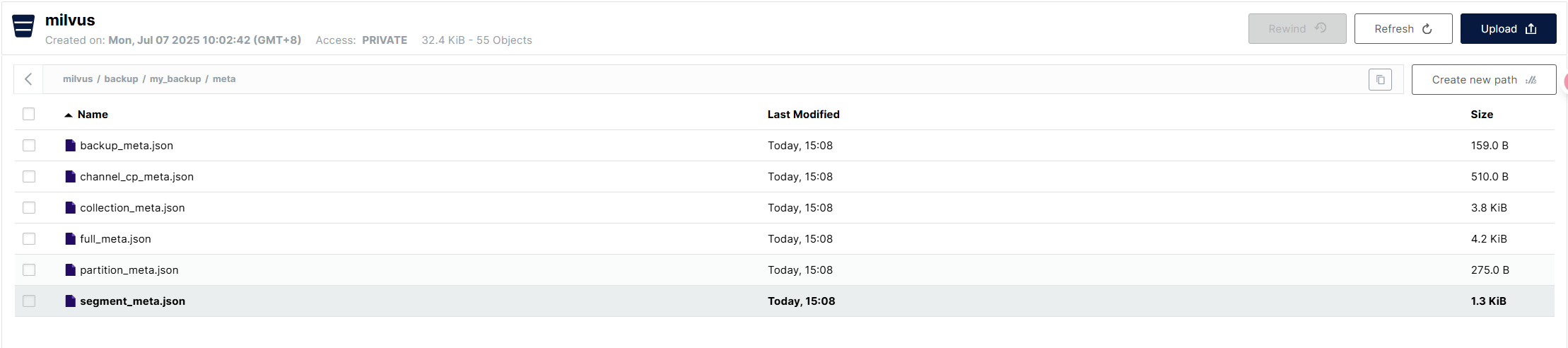
Clean Data
Delete Collection quick_setup.
- Prepare
clean-data.job.yamlapiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: milvus-clean-job
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: milvus-clean
image: m.lab.zverse.space/docker.io/bitnami/pymilvus:latest
command: ['python', '-c']
args:
- |
from pymilvus import connections, utility
import os
host = os.getenv("MILVUS_HOST")
port = os.getenv("MILVUS_PORT")
user = os.getenv("MILVUS_USER")
pwd = os.getenv("MILVUS_PWD")
collection_name = os.getenv("COLLECTION_NAME")
connections.connect("default", host=host, port=port, user=user, password=pwd)
print(f"Drop collection '{collection_name}'")
utility.drop_collection(collection_name)
env:
- name: MILVUS_HOST
value: milvus-577-proxy.middleware-csst.svc.cluster.local
- name: MILVUS_PORT
value: "19530"
- name: MILVUS_USER
value: user
- name: MILVUS_PWD
value: pwd
- name: COLLECTION_NAME
value: quick_setup
restartPolicy: Never
backoffLimit: 0 - Apply
kubectl -n middleware-csst apply -f clean-data.job.yaml
Restore
If no collection with the same name exists in the target cluster, it can be restored with its original name.If a collection with the same name exists in the target cluster, you can use the -s or --suffix parameter to set a uniform suffix. For example, quick_setup would be restored as quick_setup_recover.
- Prepare
restore.job.yamlapiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: milvus-backup-config
data:
backup.yaml: |
log:
file:
rootPath: "logs/backup.log"
milvus:
address: "milvus-577-proxy.middleware-csst.svc.cluster.local"
port: 19530
user: "uesr"
password: "pwd"
# tls mode values [0, 1, 2]
# 0 is close, 1 is one-way authentication, 2 is mutual authentication
tlsMode: 0
# Related configuration of minio, which is responsible for data persistence for Milvus.
minio:
# Milvus storage configs, make them the same with milvus config
storageType: "minio" # support storage type: local, minio, s3, aws, gcp, ali(aliyun), azure, tc (tencent), gcpnative
address: "milvus-577-minio.middleware-csst.svc.cluster.local" # Address of MinIO/S3
port: 9000 # Port of MinIO/S3
accessKeyID: "admin" # accessKeyID of MinIO/S3
secretAccessKey: "admin" # MinIO/S3 encryption string
useSSL: false # Access to MinIO/S3 with SSL
useIAM: false
iamEndpoint: ""
bucketName: "milvus" # Milvus Bucket name in MinIO/S3, make it the same as your milvus instance
rootPath: "file" # Milvus storage root path in MinIO/S3, make it the same as your milvus instance
# Backup storage configs, the storage you want to put the backup data
backupStorageType: "minio" # support storage type: local, minio, s3, aws, gcp, ali(aliyun), azure, tc (tencent)
backupAddress: "milvus-577-minio.middleware-csst.svc.cluster.local" # Address of MinIO/S3
backupPort: 9000 # Port of MinIO/S3
backupAccessKeyID: "admin" # accessKeyID of MinIO/S3
backupSecretAccessKey: "admin" # MinIO/S3 encryption string
backupBucketName: "milvus" # Bucket name to store backup data. Backup data will store to backupBucketName/backupRootPath
backupRootPath: "backup" # Rootpath to store backup data. Backup data will store to backupBucketName/ backupRootPath
backupUseSSL: false # Access to MinIO/S3 with SSL
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: milvus-restore-job
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: milvus-restore
image: m.lab.zverse.space/docker.io/milvusdb/milvus-backup:latest
command: ['sh', '-c']
args:
- |
# All collections will be restore with a suffix "_recover"
./milvus-backup restore -n my_backup --restore_index=true -s _recover --config=/data/backup.yaml
env:
- name: MILVUS_URI
value: http://milvus-577-proxy.middleware-csst.svc.cluster.local:19530
- name: MILVUS_TOKEN
value: "user:pwd"
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /data
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: milvus-backup-config
restartPolicy: Never
backoffLimit: 0 - Apply
kubectl -n middleware-csst apply -f restore.job.yaml
Check Data Restored
Because flag -s _recover has been used in backup command, collection there to be check is quick_setup_recover.
- Prepare
query-data.job.yamlapiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: milvus-query-job
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: pymilvus-query-data
image: m.lab.zverse.space/docker.io/bitnami/pymilvus:latest
command: ['python', '-c']
args:
- |
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, DataType
import os
collection_name = os.getenv("COLLECTION_NAME")
client = MilvusClient(
uri=os.getenv("MILVUS_URI"),
token=os.getenv("MILVUS_TOKEN")
)
load_state = client.get_load_state(collection_name=collection_name)
print(f"Collection '{collection_name}' current load state: {load_state}")
if load_state.get('state') != 'LoadState.Loaded':
client.load_collection(collection_name=collection_name)
print(f"Collection '{collection_name}' has loaded")
query_vector = [0.3580376395471989, -0.6023495712049978, 0.18414012509913835, -0. 26286205330961354, 0.9029438446296592]
res = client.search(
collection_name=os.getenv("COLLECTION_NAME"),
anns_field="vector",
data=[query_vector],
limit=3,
search_params={"metric_type": "COSINE"}
)
for hits in res:
for hit in hits:
print(hit)
env:
- name: MILVUS_URI
value: http://milvus-577-proxy.middleware-csst.svc.cluster.local:19530
- name: MILVUS_TOKEN
value: "user:pwd"
- name: COLLECTION_NAME
value: quick_setup_recover
restartPolicy: Never
backoffLimit: 0 - Apply
kubectl -n middleware-csst apply -f query-data.job.yaml
kubectl -n middleware-csst get pod
kubectl -n middleware-csst logs milvus-query-job-bnbp5
Best Practices
To implement scheduled backups, I provided the following prompt to the AI and asked it to expand on bakcup job. Below is the YAML output generated by the AI.
-
Change
JobtoCronJob. -
Add a shell script:
-
Create a new backup:using
milvus-backup create. -
List all backups:using
milvus-backup list. -
Delete old backups:according the max numer of backups to keep ,find and delete the old backups,using
milvus-backup delete.
- Set up the max numer of backups to keep:add a env
MAX_BACKUPS_TO_KEEPin CronJob.
Please note that this YAML has not been tested in any way and is only meant to document the thought process!
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: milvus-backup-config
data:
backup.yaml: |
log:
file:
rootPath: "logs/backup.log"
milvus:
address: "milvus-577-proxy.middleware-csst.svc.cluster.local"
port: 19530
user: "user"
password: "pwd"
# tls mode values [0, 1, 2]
# 0 is close, 1 is one-way authentication, 2 is mutual authentication
tlsMode: 0
# Related configuration of minio, which is responsible for data persistence for Milvus.
minio:
# Milvus storage configs, make them the same with milvus config
storageType: "minio" # support storage type: local, minio, s3, aws, gcp, ali(aliyun), azure, tc(tencent), gcpnative
address: "milvus-577-minio.middleware-csst.svc.cluster.local" # Address of MinIO/S3
port: 9000 # Port of MinIO/S3
accessKeyID: "admin" # accessKeyID of MinIO/S3
secretAccessKey: "admin" # MinIO/S3 encryption string
useSSL: false # Access to MinIO/S3 with SSL
useIAM: false
iamEndpoint: ""
bucketName: "milvus" # Milvus Bucket name in MinIO/S3, make it the same as your milvus instance
rootPath: "file" # Milvus storage root path in MinIO/S3, make it the same as your milvus instance
# Backup storage configs, the storage you want to put the backup data
backupStorageType: "minio" # support storage type: local, minio, s3, aws, gcp, ali(aliyun), azure, tc(tencent)
backupAddress: "milvus-577-minio.middleware-csst.svc.cluster.local" # Address of MinIO/S3
backupPort: 9000 # Port of MinIO/S3
backupAccessKeyID: "admin" # accessKeyID of MinIO/S3
backupSecretAccessKey: "admin" # MinIO/S3 encryption string
backupBucketName: "milvus" # Bucket name to store backup data. Backup data will store to backupBucketName/backupRootPath
backupRootPath: "backup" # Rootpath to store backup data. Backup data will store to backupBucketName/backupRootPath
backupUseSSL: false # Access to MinIO/S3 with SSL
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: CronJob # <--- 从 Job 修改为 CronJob
metadata:
name: milvus-daily-backup
spec:
schedule: "0 2 * * *" # <--- 定时调度:每天凌晨2点执行 (Cron 表达式)
jobTemplate: # <--- CronJob 需要包含 jobTemplate
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: milvus-backup-controller
image: m.lab.zverse.space/docker.io/milvusdb/milvus-backup:latest
command: ['/bin/sh', '-c'] # <--- 明确使用 sh 解释器
args:
- |
set -eo pipefail # 脚本出错时立即退出
BACKUP_CONFIG_PATH="/data/backup.yaml"
TIMESTAMP=$(date +%Y%m%d%H%M%S)
BACKUP_NAME="full-backup-${TIMESTAMP}" # 使用时间戳作为备份名称
echo "--- Starting Milvus backup at ${TIMESTAMP} ---"
# 1. 创建新的全量备份
echo "Creating new backup: ${BACKUP_NAME}"
./milvus-backup create -n "${BACKUP_NAME}" --config "${BACKUP_CONFIG_PATH}"
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
echo "Error: Failed to create backup. Exiting."
exit 1
fi
echo "Backup '${BACKUP_NAME}' created successfully."
# 2. 列出所有备份并按时间排序
echo "Listing existing backups..."
# milvus-backup list 命令输出格式可能不稳定,这里假设按时间降序排列
# 或者需要进一步处理输出以获取名称和时间戳
# 为了简化,这里假设`milvus-backup list`的输出每行一个备份名称,最新在上面。
# 生产环境需要更健壮的解析,例如解析JSON输出。
BACKUPS=$(./milvus-backup list --config "${BACKUP_CONFIG_PATH}" | grep -Eo 'full-backup-[0-9]{14}' | sort -r) # 提取备份名称并按降序排序(最新在前)
# 计算要保留的数量 (从环境变量获取)
MAX_TO_KEEP=${MAX_BACKUPS_TO_KEEP:-5} # 默认保留5个,如果环境变量未设置
echo "Configured to keep a maximum of ${MAX_TO_KEEP} backups."
# 3. 删除旧的备份,只保留最新的 MAX_TO_KEEP 份
COUNT=0
BACKUPS_TO_DELETE=""
for B_NAME in ${BACKUPS}; do
COUNT=$((COUNT + 1))
if [ ${COUNT} -gt ${MAX_TO_KEEP} ]; then
BACKUPS_TO_DELETE="${BACKUPS_TO_DELETE} ${B_NAME}"
fi
done
if [ -n "${BACKUPS_TO_DELETE}" ]; then
echo "Deleting old backups: ${BACKUPS_TO_DELETE}"
for DEL_NAME in ${BACKUPS_TO_DELETE}; do
echo "Deleting backup: ${DEL_NAME}"
./milvus-backup delete -n "${DEL_NAME}" --config "${BACKUP_CONFIG_PATH}" --yes # --yes 避免交互式确认
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
echo "Warning: Failed to delete backup '${DEL_NAME}'. Continuing."
fi
done
echo "Old backups deleted."
else
echo "No old backups to delete."
fi
echo "--- Milvus backup and cleanup finished ---"
env:
- name: MAX_BACKUPS_TO_KEEP # <--- 新增环境变量,控制保留数量
value: "5" # 例如,保留最新的5个全量备份
# Milvus 连接信息通过 ConfigMap 挂载的 backup.yaml 提供,以下环境变量不再需要
# - name: MILVUS_URI
# value: http://milvus-577-proxy.middleware-csst.svc.cluster.local:19530
# - name: MILVUS_TOKEN
# value: "user:pwd"
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /data # <--- 挂载 ConfigMap
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: milvus-backup-config
defaultMode: 0644
restartPolicy: OnFailure # <--- Job 失败时重启,直到成功或达到 backoffLimit
# 对于 CronJob 的 Job,通常希望失败重试,所以 restartPolicy: OnFailure 更合适
# backoffLimit: 0 意味着失败不重试,通常不推荐用于定时任务
# 如果希望失败重试 N 次,可以设置 backoffLimit: N (默认6次)